Wireless¶
The wireless interface may vary slightly from model to model. For example, some models do not have 5 GHz Wi-Fi, such as GL-MT300N-V2 (Mango) and GL-X300B (Collie); some do not include Wi-Fi capability, such as GL-MT2500/GL-MT2500A(Brume 2).
Wi-Fi Status Display¶
GL.iNet router’s Wi-Fi networks are enabled by default, and the corresponding Wi-Fi icon will light up below the device model image on the INTERNET page.
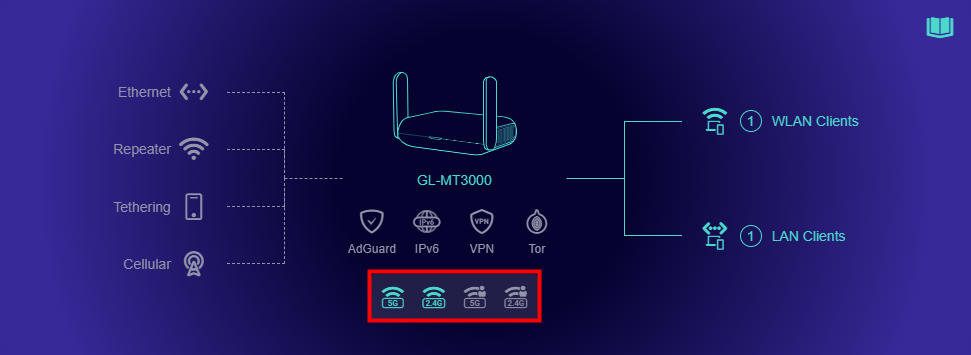
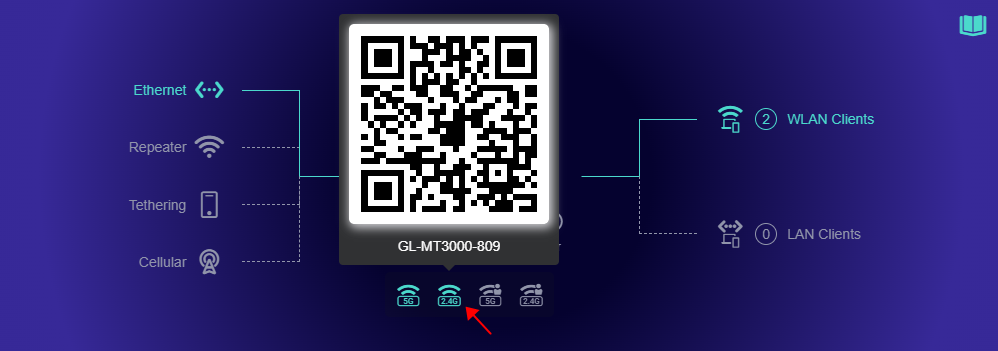
The Wi-Fi QR code will be displayed if the cursor hovers over the enabled Wi-Fi icon. You can scan the Wi-Fi QR code using your Phone/Pad to quickly connect to the corresponding Wi-Fi.
Wireless Settings¶
On the left side of the web Admin Panel, go to WIRELESS.
The wireless page supports setting up different Wi-Fi configurations, and it includes various Wi-Fi bands such as 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz, and MLO Wi-Fi (which varies by router model), with each band further divided into Main Wi-Fi and Guest Wi-Fi networks for flexible wireless network management.
MLO Wi-Fi¶
| Supported Models | |
|---|---|
| Slate 7 Pro (GL-BE10000) | √ |
| Beryl 7 (GL-MT3600BE) | √ |
| Flint 3e (GL-BE6500) | √ |
| Flint 3 (GL-BE9300) | √ |
| Slate 7 (GL-BE3600) | √ |
MLO (Multi-Link Operation) is one of the core features of Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be), designed to improve network performance, significantly reduce latency, and enhance connection stability by utilizing multiple frequency bands simultaneously such as 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz.
Click on the tabs below to learn about MLO Main Wi-Fi and MLO Guest Wi-Fi settings.
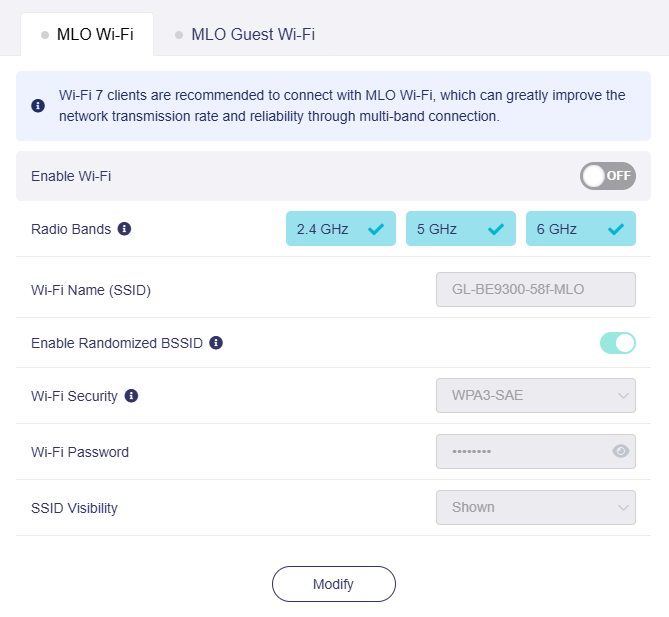
The MLO Main Wi-Fi allows you to configure multiple settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, selecting radio bands (at least two), enabling/disabling randomized BSSID, setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, Wi-Fi password, and SSID visibility.
-
If the MLO Wi-Fi radio bands include 6 GHz, the MLO Wi-Fi BSSID will synchronize when the 6GHz Wi-Fi BSSID changes.
-
The default Wi-Fi security for MLO Wi-Fi is WPA3-SAE, which is suitable for most devices that support MLO.
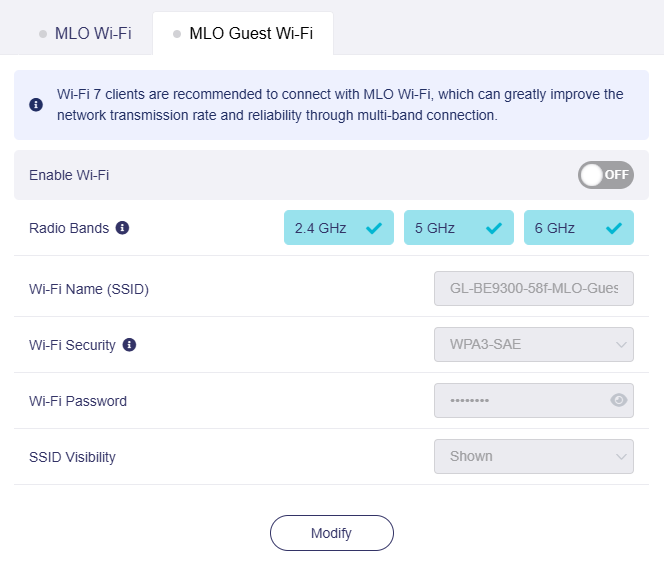
The MLO Guest Wi-Fi allows you to configure simplified settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, selecting radio bands (at least two), setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, password, and SSID visibility.
6 GHz Wi-Fi¶
| Supported Models | |
|---|---|
| Slate 7 Pro (GL-BE10000) | √ |
| Mudi 7 (GL-E5800) | √ |
| Flint 3 (GL-BE9300) | √ |
The 6 GHz Wi-Fi provides faster, more stable wireless connectivity with reduced congestion compared to 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Click on the tabs below to learn about 6 GHz Main Wi-Fi and 6 GHz Guest Wi-Fi settings.
The 6 GHz Main Wi-Fi allows you to configure multiple settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, setting TX power, enabling/disabling randomized BSSID, setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, Wi-Fi password, SSID visibility, Wi-Fi mode, bandwidth, and channel.
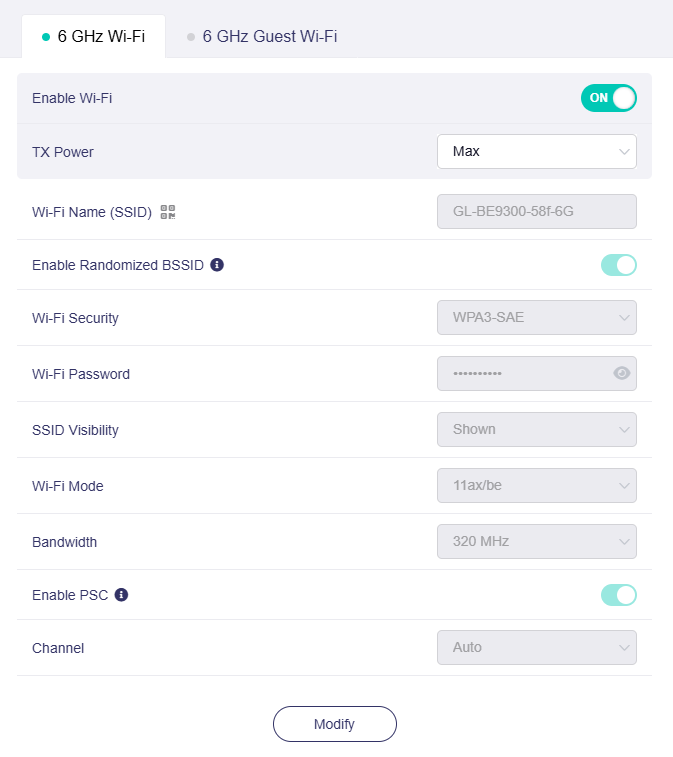
- Enable PSC: When PSC (Preferred Scanning Channel) is enabled, only channels with higher connectivity will be reserved to ensure 6 GHz device connections.
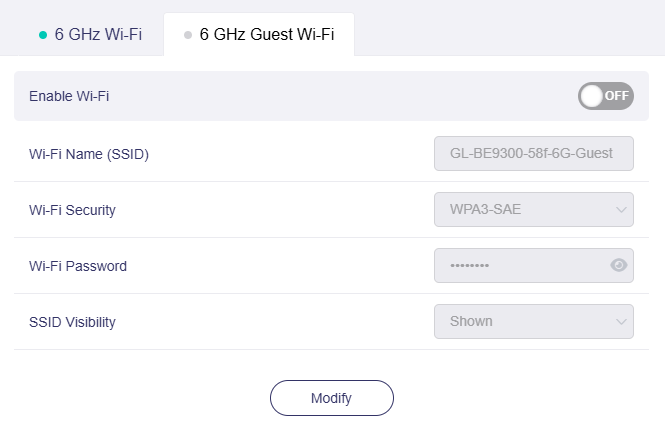
The 6 GHz Guest Wi-Fi allows you to configure simplified settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, password, and SSID visibility.
5 GHz Wi-Fi¶
Click on the tabs below to learn about 5 GHz Main Wi-Fi and 5 GHz Guest Wi-Fi settings.
The 5 GHz Main Wi-Fi allows you to configure multiple settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, setting TX power, enabling/disabling randomized BSSID, setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, Wi-Fi password, SSID visibility, Wi-Fi mode, bandwidth, and channel.

The 5 GHz Guest Wi-Fi allows you to configure simplified settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, password, and SSID visibility.

2.4 GHz Wi-Fi¶
Click on the tabs below to learn about 2.4 GHz Main Wi-Fi and 2.4 GHz Guest Wi-Fi settings.
The 2.4 GHz Main Wi-Fi allows you to configure multiple settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, setting TX power, enabling/disabling randomized BSSID, setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, Wi-Fi password, SSID visibility, Wi-Fi mode, bandwidth, and channel.

The 2.4 GHz Guest Wi-Fi allows you to configure simplified settings, including enabling/disabling Wi-Fi, setting the Wi-Fi name (SSID), Wi-Fi security, password, and SSID visibility.

Note¶
-
The Wi-Fi QR code will be displayed beside the SSID if the cursor hovers over the QR code icon. You can scan the Wi-Fi QR code to quickly connect to the corresponding Wi-Fi.

-
Randomized BSSID: This feature is enabled by default. It aims to prevent the client vendors from collecting nearby Wi-Fi BSSIDs and client devices' GPS coordinates to their servers. Click here for more details.
-
The Bandwidth and Channel cannot be modified when the router acts as a repeater, as they follow that of the repeated network.
-
When Channel is set to Auto, the router's Wi-Fi will not automatically switch to the DFS channel.
-
When switching the Channel to a DFS one from non-DFS channel, a caution will appear as follows.

-
When the Bandwidth is set to 160 MHz (Only available on some models), the Wi-Fi will always use the DFS channel, even if you choose a non-DFS channel or Auto for Channel settings.
Randomized BSSID¶
Randomized BSSID has been available since firmware v4.6. It aims to prevent the client vendors from collecting nearby Wi-Fi BSSIDs and client devices' GPS coordinates to their servers.
How Client Vendors Collect Location Data
Client vendors usually collect the geographical location data of Wi-Fi access points by leveraging their unique BSSIDs to locate devices. When client devices (e.g., mobile phones, computers) scan or connect to a router:
-
If other devices are within the router’s Wi-Fi signal coverage, their location and movement trajectories may be exposed.
-
If a device uses GPS for positioning, it periodically uploads nearby Wi-Fi BSSIDs and corresponding GPS coordinates to the vendor’s server.

Security Risks of Crowdsourced Tracking
Even devices without GPS (or with GPS disabled) can estimate their location by querying visible BSSID info. However, this crowd-sourced location tracking system has security vulnerabilities. Attackers can use it to accumulate a global database of Wi-Fi access point locations and continuously track the movement trajectories of devices, posing a threat to user privacy and security.
How Randomized BSSID Protects Your Privacy
To address these vulnerabilities, GL-iNet routers implement the Randomized BSSID feature as a privacy safeguard.
In the router’s web admin panel, go to WIRELESS -> 5GHz Wi-Fi or 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, the BSSID option is enabled by default.
With this setting, the device uses a randomly generated BSSID and renews it each time it boots. If you disable the random BSSID, the router reverts to using the real MAC address.
Note: For Guest Wi-Fi, the BSSID remains consistent with the Main Wi-Fi BSSID within the same frequency band.
Still have questions? Visit our Community Forum.