How to route VPN Client DNS queries to the VPN Server's Upstream DNS?¶
This tutorial introduces the steps to redirect all DNS queries from VPN clients to your self-hosted DNS Server on the LAN side of your primary router, upstream of the VPN server.
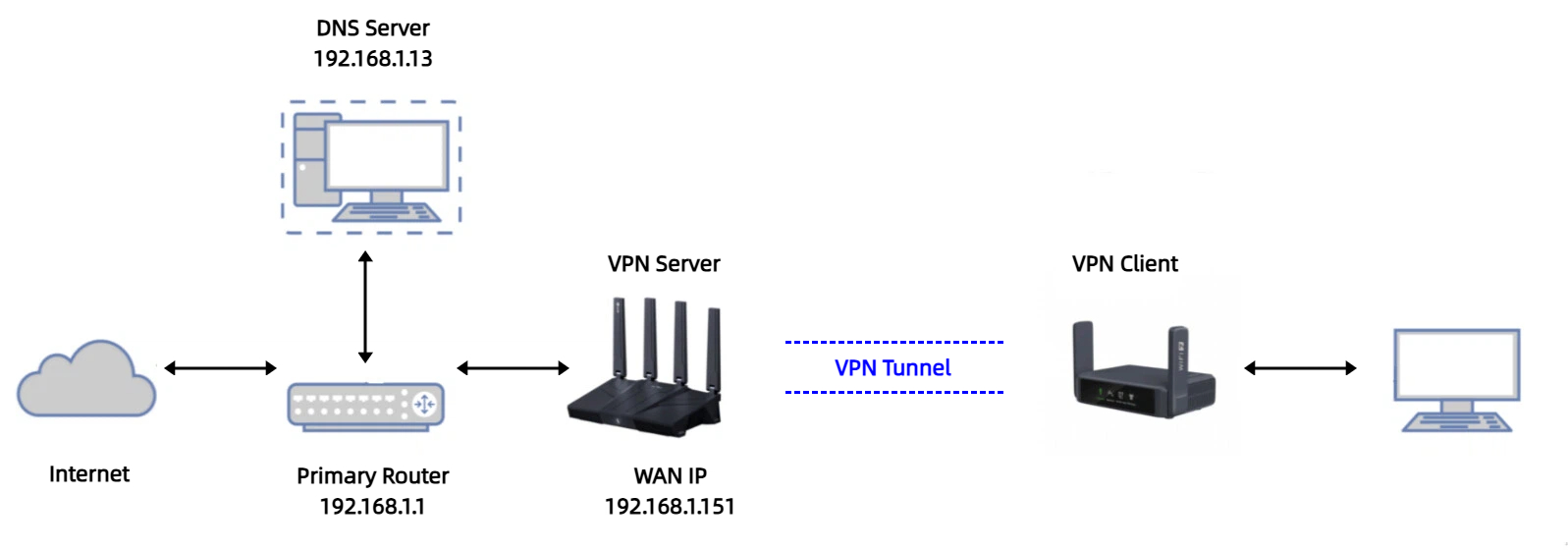
Topology¶
In this tutorial, we use Flint 3 (GL-BE9300) and Slate 7 (GL-BE3600) as examples.
Flint 3 is the VPN server, which has a primary router on its upstream network, and Slate 7 is the VPN client connecting to Flint 3.
When a VPN tunnel is established between the VPN server and client, by default, the DNS queries from the VPN client are first sent to the VPN server, then forwarded to the primary router, and finally resolved by the ISP-assigned DNS servers configured on the primary router's WAN.

However, if you have deployed a self-hosted DNS Server (IP address 192.168.1.13) on the primary router, additional configurations are required to route DNS queries to your self-hosted DNS Server.
Setup¶
-
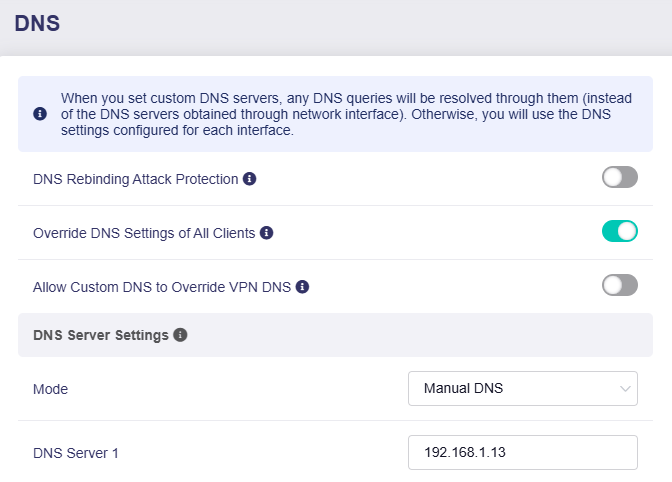
Log in to the Flint 3's web Admin Panel, navigate to NETWORK -> DNS. Switch the DNS Server Mode to Manual DNS, and enter the IP address of your DNS Server.
-
Navigate to VPN -> WireGuard Server -> Configuration tab, note the IPv4 Address, which is usually
10.0.0.1/24or10.1.0.1/24, depending on models and firmware versions.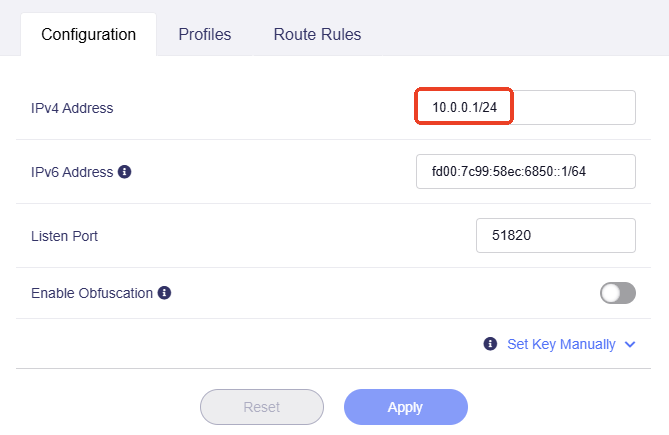
-
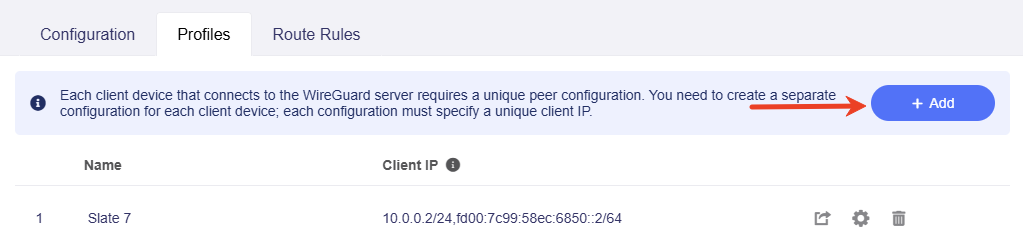
Switch to the Profiles tab, add a client configuration and export a profile for Slate 7.
-
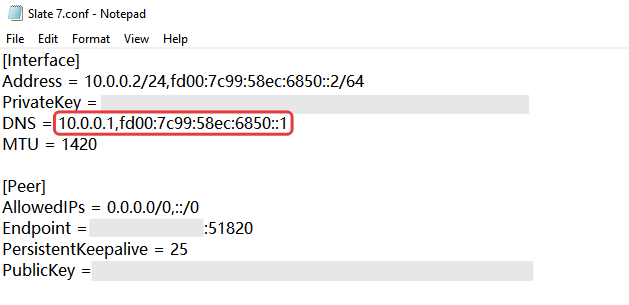
Open the profile, make sure the DNS is the VPN Server IP address you obtained in step 2.
To avoid DNS resolution failure, please delete "64.6.64.6" if any, and save the changes.
-
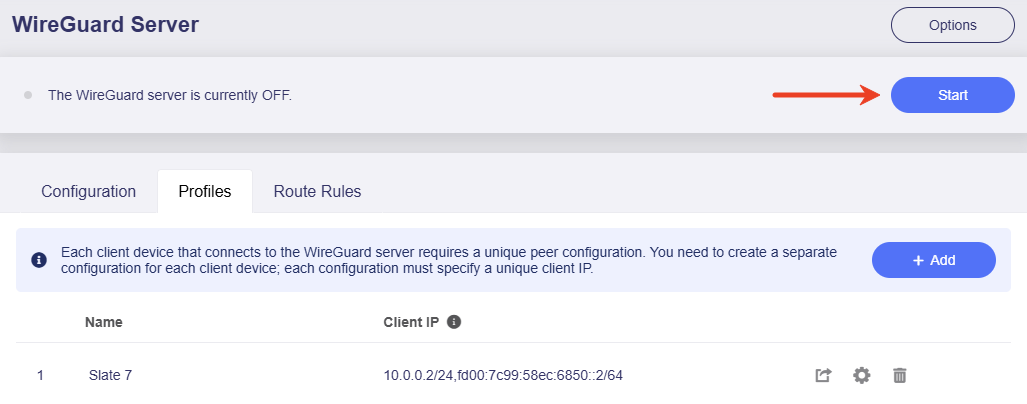
On the Flint 3's web Admin Panel, click the Start button on the top of the WireGuard Server page to run the server.
-
Log in to the Slate 7's web Admin Panel, navigate to VPN -> WireGuard Client.
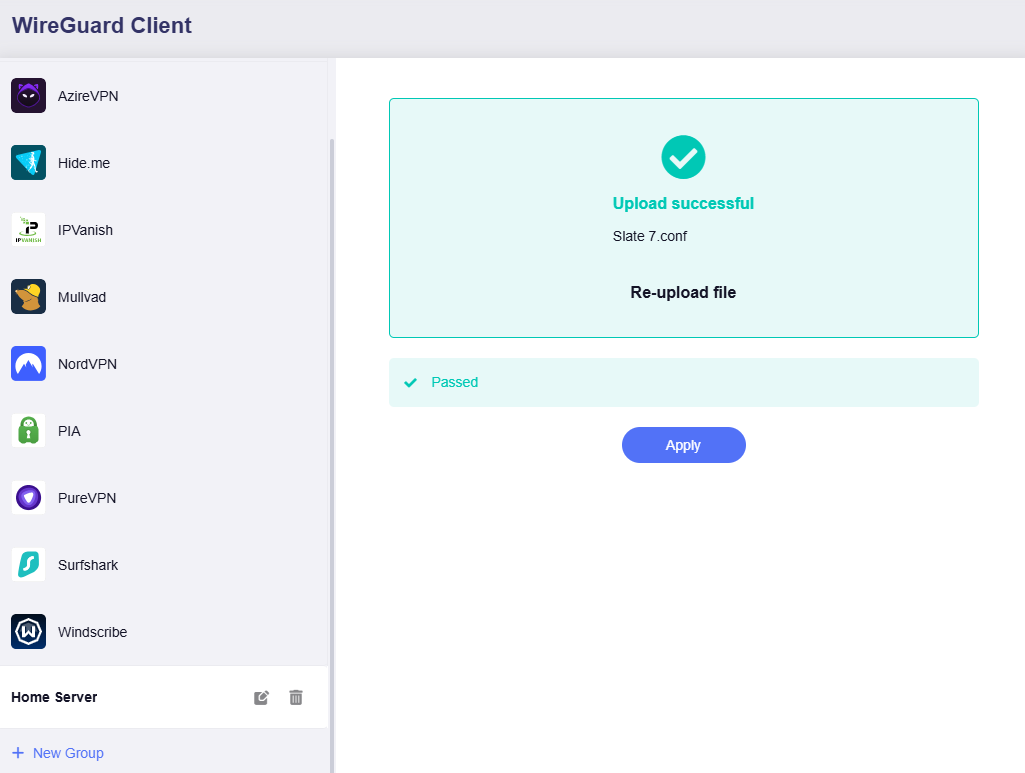
Click Add Manually and upload the edited profile.
-
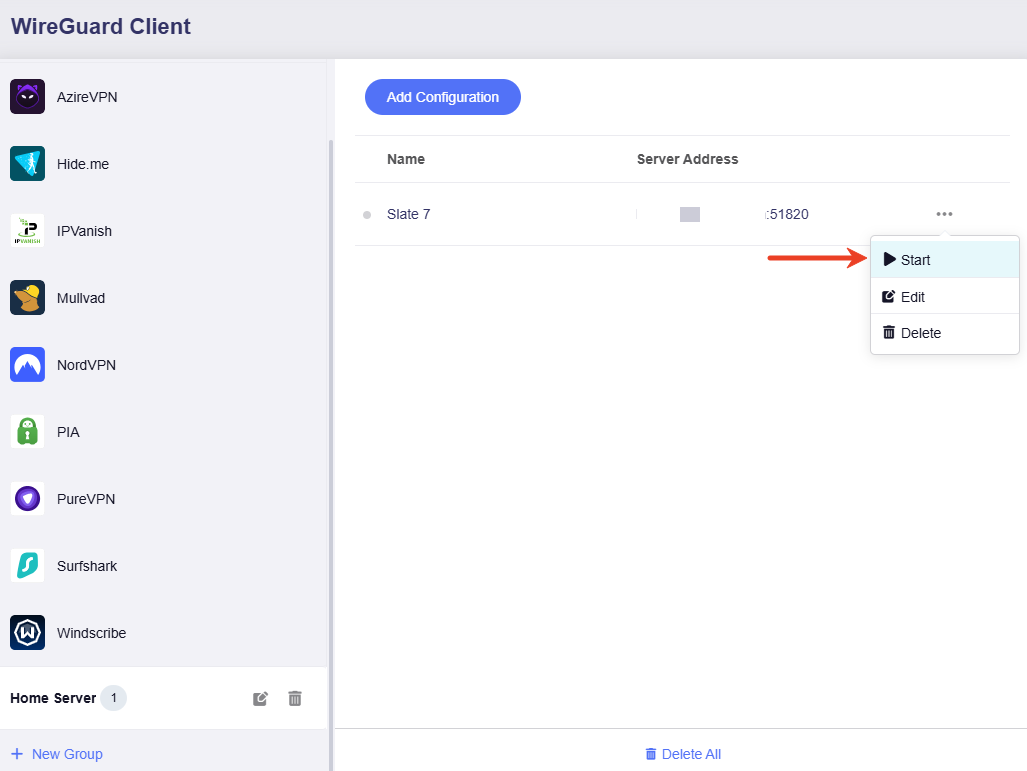
Click the three-dot icon to start the VPN connection. If the status indicator turns green, it means the VPN connection is successful.
Verify DNS resolution¶
Run the following command to capture DNS traffic on the VPN client. It will show that all VPN client DNS traffic goes to the VPN server (i.e., 10.0.0.1 in this example).
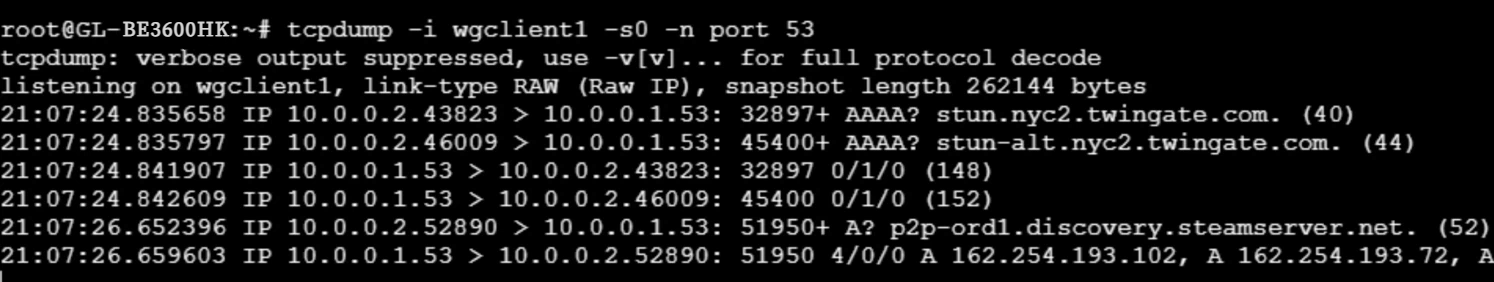
Run the following command to capture DNS traffic on the VPN server. It will show that all VPN client DNS traffic finally goes to the self-hosted DNS server (i.e., 192.168.1.13 in this example).
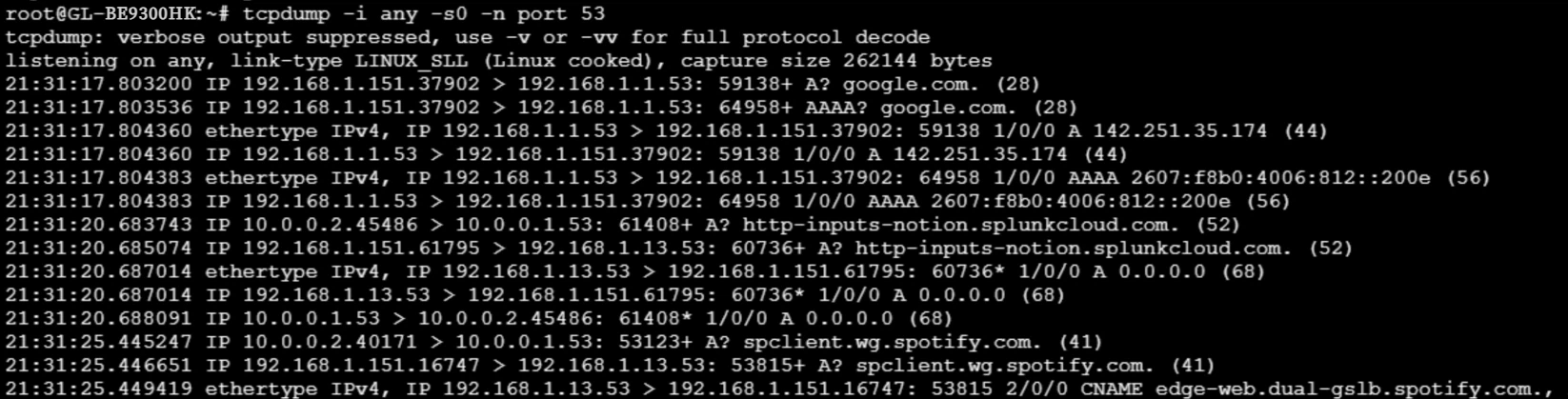
Still have questions? Visit our Community Forum or Contact us.